SEAMLESS TUBES
STAINLESS STEEL • NICKEL ALLOYS • TITANIUM • TITANIUM ALLOYS
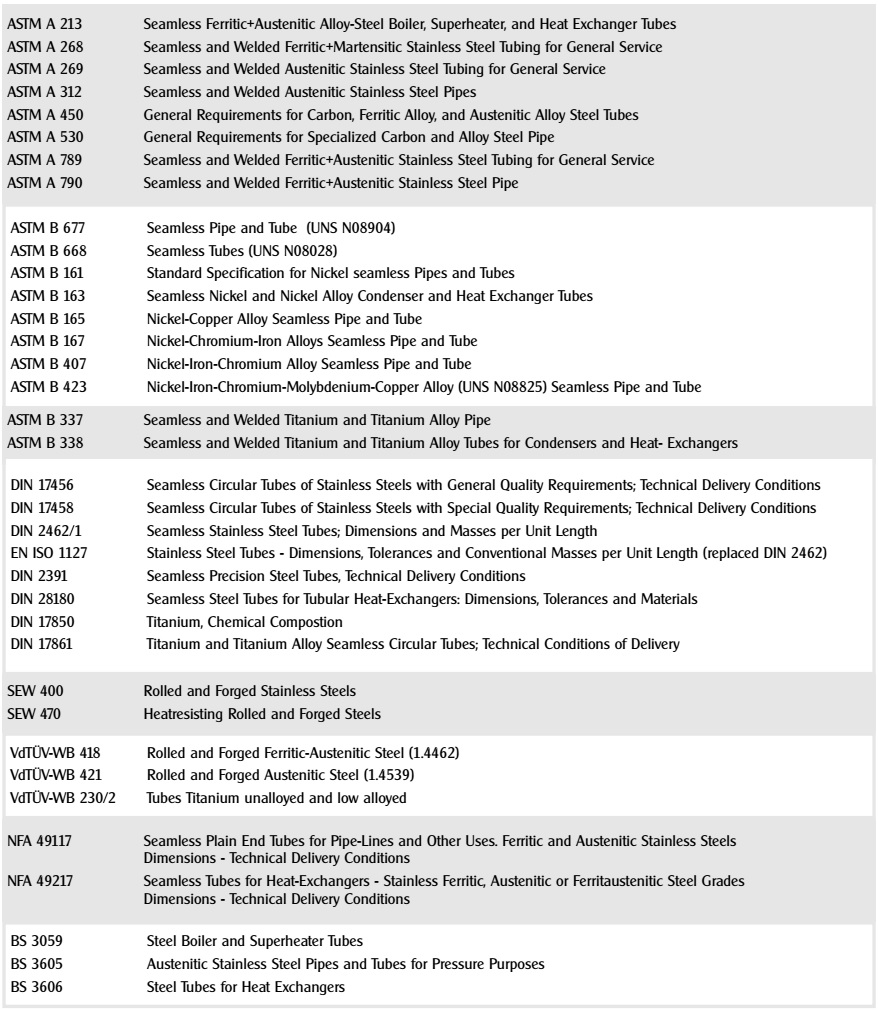
The Standars
SELECTION DATA
Standard Grades - Composition - Applications - Properties

1. AUSTENITIC STEELS
TP 304=UNS S30400=1.4301=
TPS-INOX-4301-304
The most popular stainless steel has an economic balance of alloying elements to ensure its good cold formability, corrosion resistance, toughness and good mechanical properties with no excessive work-hardening. It performs well in unpolluted atmospheres but can tarnish or lightly rust in damp atmospheres around some industrial and on/offshore locations. The steel has been used extensively for potable water tubing and in fresh feedwater systems where precautions are taken to avoid crevice attack under deposits, etc. Performance in aerated seawater is not good without adequate galvanic or cathodic protection. Stability and toughness at cryogenic temperatures is high.
TP 304H=UNS S30409= TPS-INOX-304H
TP 304H with guaranteed carbon content of min. 0,04% which gives a better creep resistance. Similar oxidation resistance to TP 304. Main applications: Heat exchangers, chemical and petrochemical furnaces.
TP 304L=UNS S30403=1.4306=
TPS-INOX-4306-304L
Low carbon version of TP 304 guaranteed no creep resistance above 500°C. Good high temperature oxidation resistance up to 900°C. General corrosion characteristics are similar to TP 304. Stability and toughness at cryogenic temperatures is high. Main applications: Pipe and heat exchanger tubes in chemical, petrochemical and food industries.
TP 316/TP 316L=UNS S31600/31603=1.4401/1.4404= TPS-INOX-4401/4404-316/316L
These grades belong to the family of 17%Cr12-13%Ni steels containing 2,0-3,0%Mo. This standard grade is used where specific attributes of other members of the family are not necessary - eg. no likelihood of intercrystalline corrosion caused by welding. Special for TP 316L, low carbon content, minimizes chromium carbide preciptation and improves resistance to intercrystalline corrosion. After TP 304/304L type steels, these TP 316/316L grades are the most widely used austenitics. Good high temperature oxidation resistance up to 900°C. In the damp industrial or onshore atmospheres of Europe, they perform better than TP 304/304L and ferritic grades. In low temperature seawater they offer limited resistance to pitting but are susceptible to crevice attack. Their short- and long-time properties at elevated temperatures are also superior to those of comparable TP 304/304L grades. Main applications: Pipe and heat exchanger tubes in chemical and petrochemical plant, in boilers and food industry.
TP 316H=UNS S31609= TPS-INOX-316H
This grade with guaranteed carbon content of min. 0,04% enhances strength at elevated temperatures. Similar oxidation resistance to TP 316. Main applications: Heat exchangers, furnaces, chemical and petrochemical plant.
TP 321=UNS S32100=1.4541= TPS-INOX-4541-321
High carbon steels prone more to intercrystalline attack in weld zones and slower cooling sections. These steel avoids such attacks through its stabilization with Ti. The corrosion behaviour of this alloy in natural environments is very similar to the TP 304/304L alloys. Architecturally, it may not be adequate for near-industrial or onshore locations in Europe. Satisfactory in many low-chloride waters, it is prone to pitting or crevice corrosion in seawater. Water treatment, galvanic protection and deaeration can influence the performance.
TP 321H=UNS S32100=1.4878= TPS-INOX-4878-321H
This is the high carbon version of TP 321 which ensures greater creep resistance. Behaves much the same as TP 321 in oxidation resistance. Main applications: Heat exchangers, furnaces, boilers in chemical and petrochemical plant.
TP 316Ti=UNS S31635=1.4571= TPS-INOX-4571-316Ti
This is one of the family of 17%Cr12-13%Ni steels containing Mo of 2,0-2,4% stabilized with Ti which minimizes chromium carbide precipitation and improves resistance to intergranular corrosion. In the damp industrial or coastal atmospheres of Europe, they perform better than TP 304/304L and ferritic grades. In low temperature seawater they offer limited resistance to pitting but are susceptible to crevice attack. Their short- and long-time properties at elevated temperatures are also superior to those of comparable TP 304/304L grades.
2. Super-Austenitic Steels
TP 904L=UNS N08904=1.4539= TPS-Technichromo 904L
This high-alloy austenitic is very resistant to attack from diluted sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid and acetic acid. It resists pitting in neutral chloride solutions. Its resistance to stress corrosion cracking in some hot chlorides is much superior to that of the lower nickel austenites. This steel has good formability and weldability. This material is present in all common standards like ASTM, DIN, BS and NFA, however with some differences. Design stresses up to 370°C are included in ASME II.
